Welcome to B.K Speech Therapy
We deal with all kind of speech languages disorder,disability Handicap impairiment present in pediatrics & adult population. We are dedicated to helping clients and their families with utmost professionalism.
Phonological disorder2-Motor deficit,Cognitive deficit,Learning disability,Autism spectrum disorder,Attention deficit/hyperactive disorder,Hearing impairment-Auditory-verbal therapy,Dementia,dysarthria,dysphagia.,Delay speech language,Speech language communication problem,stuttering,misarticulations,Oro-motor Therapy,Communication therapy,Language/Speech therapy,Pure Tone Audiometry,Hearing testing,Advance digital Hearing Aid,Speech language therapy is concerned with the disorder of ,Speech language,communication on voice,swallowing problems in adults&children
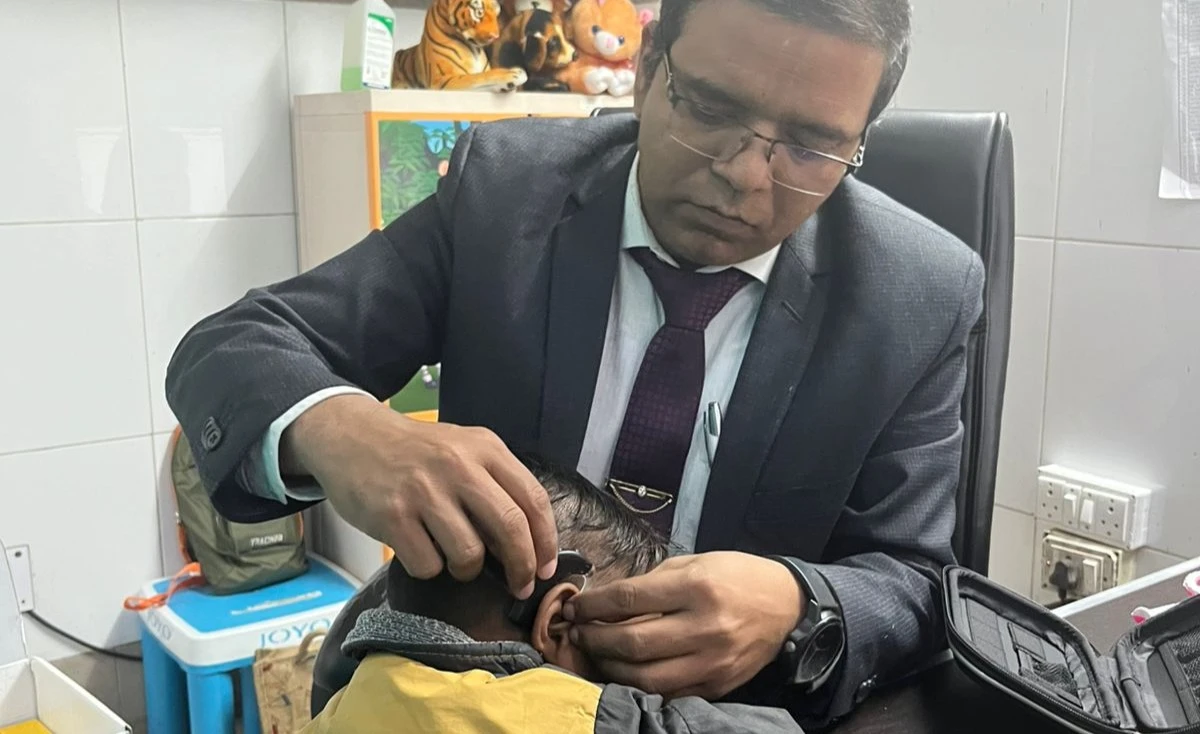

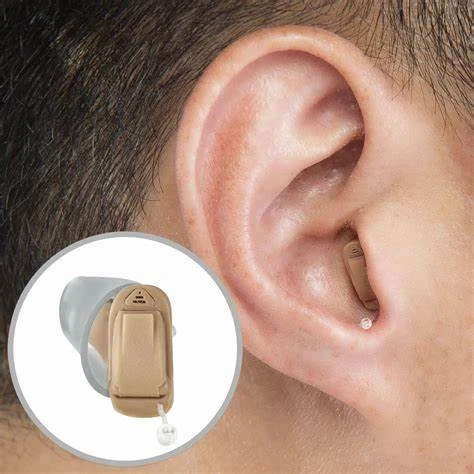
Cic hearing aid
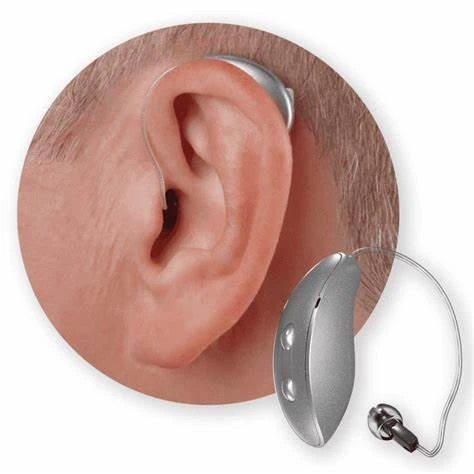
Ric hearing aid

Iic hearing aid
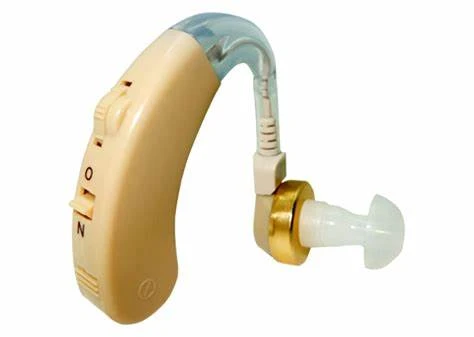
Bte hearing aid

Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders affecting movement and posture due to brain damage during development, often before or shortly after birth. Causes range from genetic factors and birth injuries to infections and premature birth. Symptoms vary widely, including motor impairments like stiffness or poor coordination, neurological issues such as learning disabilities, and physical complications. Diagnosis involves observing development and medical tests. While there's no cure, treatments like physical, occupational, and speech therapy, along with medications and surgery, help manage symptoms and improve life quality. Early intervention is crucial for better outcomes.

Down syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by a full or partial extra copy of chromosome 21. It leads to developmental delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability, and distinct physical features. Common physical traits include a flattened face, upward slanting eyes, small ears, and weak muscle tone. The risk of Down syndrome increases with maternal age. It is typically caused by a random error in cell division, not by inherited factors. The three types of chromosomal changes that can cause Down syndrome are complete trisomy 21, mosaic trisomy 21 and translocation trisomy 21. There is no cure, but early care can help individuals live full lives.

Autism, or autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a complex developmental condition affecting social interaction, communication, and behavior. It typically manifests before age three and persists throughout life. Individuals with autism may struggle with understanding social cues, maintaining eye contact, and expressing emotions. They often exhibit restricted and repetitive behaviors, such as fixating on specific interests or adhering to routines. The severity of symptoms varies widely among individuals. While the exact causes are not fully understood, both genetic and environmental factors are believed to contribute. Early intervention can significantly improve development and daily functioning for those with autism.

Stuttering, also known as stammering, is a speech disorder characterized by disruptions in the flow of speech, including repetitions of sounds or syllables and prolonged sounds. It commonly begins in children aged 2 to 6 as they develop language skills, with boys being more affected than girls. While many children outgrow it, some continue to stutter into adulthood. Causes are not fully understood but may include genetic factors, neurophysiological issues, and environmental influences like stress. Treatment options include speech therapy and techniques to improve fluency and confidence in communication.
Aphasia is a communication disorder that affects an individual's ability to use and understand language, resulting from damage to the brain areas responsible for language processing. It often occurs after a stroke or brain injury but can also develop gradually due to conditions like dementia or brain tumors. Symptoms vary widely and may include difficulties in speaking, writing, reading, and understanding spoken language. There are different types of aphasia, such as expressive aphasia (difficulty expressing thoughts) and receptive aphasia (difficulty understanding language). Treatment typically involves speech and language therapy to help individuals regain communication skills.
Dysarthria is a speech disorder resulting from muscle weakness affecting the control of speech production. It can arise from neurological damage due to conditions such as stroke, brain injury, or neurodegenerative diseases. Symptoms include slurred or slow speech, difficulty controlling volume, and changes in voice quality (e.g., nasal or strained). Individuals may also experience challenges with chewing and swallowing. Dysarthria is distinct from other language disorders like aphasia, which affects comprehension and language production. Treatment typically involves speech therapy to improve communication abilities, although the condition itself may not be fully reversible.

Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. It typically manifests in childhood and can continue into adulthood. ADHD is categorized into three types: predominantly inattentive, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive, and combined presentation. Symptoms may include difficulty focusing, excessive talking, impulsive decision-making, and challenges with organization. The exact cause is not fully understood but involves genetic and environmental factors. While there is no cure, effective treatments such as behavioral therapy and medication can help manage symptoms and improve daily functioning in affected individuals.
A cerebrovascular accident (CVA), commonly known as a stroke, occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, leading to oxygen deprivation and the death of brain cells. There are two main types: ischemic strokes, caused by blockages, and hemorrhagic strokes, caused by ruptured blood vessels. Symptoms include weakness, paralysis on one side of the body, speech problems, and loss of balance. Risk factors include high blood pressure, diabetes, heart disease, smoking, and a family history of stroke. Immediate medical attention is crucial to minimize brain damage and improve prognosis.

Childhood trauma involves adverse experiences like abuse, neglect, or witnessing violence that threaten a child's sense of safety and well-being. Over two-thirds of children experience a traumatic event by age 16. These experiences can have lasting psychological, physiological, and sociological impacts. Trauma can affect physical health, mental health, cognitive abilities, self-esteem, emotional regulation, and relationships. Young children are especially vulnerable due to their developing brains. Reactions to trauma can include emotional upset, anxiety, behavioral changes, and difficulties with self-regulation. However, a positive caregiver can help shield children from long-term harm. Psychotherapy can aid in healing and managing the effects of childhood trauma.
